This article by Alexander Novak was published 14 April 2023 in Energy Policy as was the previous. It provides some of the basis for the next article dealing with energy in the overall Arctic. It’s not as long as the previous. There are many videos of Russia’s icebreakers online. This 20 minute video about the construction of the Leader Class Icebreakers demonstrates the complexity of this engineering project. Now to get to the article. All formatting original:
The Arctic zone of the Russian Federation has huge reserves of minerals – oil, gas, coal, as well as rare metals, stones and minerals, including gold and diamonds. For the full development of these natural resources and their realization, it is necessary to have a convenient, accessible and cost-effective transport corridor. The Northern Sea Route (NSR) is the only waterway that connects all subarctic and arctic regions of Russia. In addition, the NSR is currently the shortest and most promising route between Europe and Asia, which is an additional incentive for the development of key industries in the Russian North and makes the transport corridor increasingly attractive for both investors and cargo carriers.
History of the Northern Sea Route
Researchers and traders became interested in the modern route of the Northern Sea Route as early as the 13th and 16th centuries. The first through voyage from east to west with wintering near the Taimyr Peninsula was made at the end of the first quarter of the 20th century, and in 1932 the route was completed in one navigation. A year later, the first transport from Leningrad to Vladivostok took place. In the 1970s and 1980s, the development of the Northern Sea Route was carried out at an increasingly active pace, which was largely made possible by the formation of the world's only nuclear-powered icebreaker fleet. In 1991, the Northern Sea Route was opened for international navigation.
Today, the length from the Kara Strait to the Bay of Providence is 5.6 thousand km. The shipping route passes through six seas of the Arctic Ocean: the Barents, Kara, Laptev, East Siberian, Chukchi and Bering Seas. Transporting goods from Asia to Europe via the Northern Sea Route takes about a third less time than shipping through the Suez Canal.In Soviet times, a record volume of traffic on the NSR was reached in 1987 – 6.6 million tons, while over the past six years, cargo traffic on the NSR has more than tripled and exceeded 34 million tons (in 2017 – 10.7 million tons), which is 2 million tons higher than the target value. In 2022, the capacity of existing ports and terminals on the Northern Sea Route amounted to more than 32 million tonnes.
Regulatory and regulatory framework for the development of the Northern Sea Route
The Government of the Russian Federation pays special attention to the development of the route. The President of Russia has set the task of creating a modern competitive logistics system on the basis of the Northern Sea Route, which will become a driver for the development of the Arctic region of our country. To this end, in recent years, a number of strategic documents have been developed, the necessary management decisions have been made, and effective interaction of all participants in the process has been organized.
Currently, the federal project "Development of the Northern Sea Route" is being implemented. Its task is to expand the infrastructure that will ensure effective territorial connectivity between the Far East and the western regions of Russia and year-round navigation along the Northern Sea Route. It also provides for the introduction of unmanned technologies in cargo transportation and navigation, as well as a sustainable increase in the environmental friendliness of energy and transport.In accordance with the instructions of the President of the Russian Federation, in August last year, the Northern Sea Route Infrastructure Development Plan for the period up to 2035 was approved. The document contains 152 measures divided into 5 blocks: cargo base, transport infrastructure, cargo and icebreaker fleet, safety of navigation along the Northern Sea Route, management and development of navigation along the Northern Sea Route.
In 2022, a single navigation control center was established in the NSR water area under the leadership of Rosatom State Corporation. This makes it possible to introduce the principle of a "single window" for the issuance and suspension of permits for navigation of vessels, the coordination of areas for hydrographic works, the centralization of the development of navigation routes and the issuance of recommendations to vessels, and the accumulation of data on hydrometeorological and ice conditions.
Such measures will improve the safety of navigation in difficult ice conditions, ensure the stable operation of the transport route, including the delivery of goods within the framework of the Northern Delivery, during which fuel and food are supplied to regions that do not have year-round land communication with the rest of the country.
In order to regularly coordinate the actions of federal and regional executive authorities and industry companies in the development of the Northern Sea Route, in accordance with the instructions of the Prime Minister of the Russian Federation, work has been organized on the basis of the Coordination Center under the Government of the Russian Federation. As part of this cooperation, comprehensive monitoring of the construction of ships and icebreakers, the implementation of infrastructure projects, the progress of the Northern Delivery, and the current situation on the Northern Sea Route is assessed. This allows us to make timely effective decisions for the successful implementation of tasks for the development and operation of the route.
Prospects for increasing cargo traffic
At present, the development of regular container traffic between the western and eastern parts of the Russian Federation continues. A significant part of export cargo traffic is being reoriented to the markets of the Asia-Pacific region.
Further prospects for increasing cargo traffic on the NSR are associated with the implementation of a number of major projects in the oil and gas industry, in the field of non-ferrous metals mining, as well as the development of port infrastructure.
Despite the fact that due to external pressure and sanctions restrictions, Russian companies were forced to postpone the commissioning of a number of major projects, all of them are under implementation and, I am sure, will be successfully completed.
Today, more than half of the NSR's cargo traffic is liquefied natural gas, and here we see a high potential for development, as LNG continues to increase its share in the global market, including growing supplies from Russia. The production of liquefied natural gas in our country increased by almost 14% in 2020–2022. At the end of 2022, LNG production in Russia reached a record 45.9 billion m3.The NSR route is home to Russia's key existing and prospective liquefied natural gas production projects. NOVATEK is shipping products from the Yamal LNG plant as planned. Work continues on the construction of the Arctic LNG-2 production complex. For the needs of the project, the Utrenny terminal is being built in the Gulf of Ob. The company plans to implement the Arctic LNG-1, Arctic LNG-3, Ob Gas Chemical Complex, and Yurkharovneftegaz projects. In Bechevinskaya Bay on the Kamchatka Peninsula, NOVATEK's LNG transshipment terminal is under construction.
Gazprom Neft continues to implement a project to export oil from the Novy Port field. In 2024, the company plans to produce 5.08 million tons of raw materials.
Norilsk Nickel uses the Northern Sea Route to export the products of its enterprises, as well as to transport supply cargo. In 2023, it is planned to export 2.3 million tons of cargo along the Northern Sea Route, in 2024 - already 2.4 million tons.The first batch of coal was shipped in October 2022, and it is planned to export 3.5 million tons in 2024, and 10 million tons from 2030.In Taimyr in the Yenisei Bay, Vostok Oil LLC is building the Sever Bay port, which is designed to organize infrastructure for the production and export of crude oil from its fields.
According to the company, by 2024, the volume of cargo traffic along the NSR will grow to 30 million tons.In 2019, a decision was made to develop deposits in the Baim ore zone, involving the construction of a mining and processing plant and all the necessary infrastructure.
Starting this year, it is planned to start the delivery of construction materials for the project. From 2029, the transportation of finished products will amount to 1.809 million tons. In 2030, it is planned to transport 1.863 million tons.
As part of the project, it is planned to build a marine terminal in the port of Pevek in Chukotka, three quarters of the capacity of which will be copper concentrate from the Peschanka deposit of the Baim Mining and Processing Plant. Hydraulic engineering works will be carried out to place floating nuclear power units to supply electricity to the copper mining enterprise in Peschanka. The implementation of the announced investment projects in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation until 2035 will ensure GDP growth of more than 30 trillion rubles. And it will bring more than 10 trillion rubles in additional tax revenues.
Arctic Icebreaker and Cargo Fleet
The availability of a modern icebreaker fleet is the basis for the successful development of the Northern Sea Route. On behalf of the President of Russia, work is underway to create a line of the most powerful icebreakers in the world, which will ensure year-round navigation on the route.
Serial production of new Project 22220 nuclear-powered icebreakers has been launched. As part of this project, three icebreakers have already been commissioned, and four are under construction.In particular, in November last year, a new universal nuclear-powered icebreaker "Ural" was put into operation, which is capable of operating both in deep water and in riverbeds, thereby replacing two types of icebreakers. Its main power plant consists of two RITM-200 reactors with a thermal capacity of 175 MW each. The main advantage of the RITM-200 reactor plant over other similar units is its compactness and cost-effectiveness.
The serial universal nuclear-powered icebreaker Yakutia was launched. It is expected that the icebreaker will be put into operation by the end of 2024. Contracts have been signed for the construction of two additional icebreakers of Project 22220. I would like to emphasise that the share of domestic materials and equipment in the manufacture of vessels of this series is more than 90%. Particular attention is focused on the construction of the innovative super-icebreaker Rossiya of project 10510 (Leader) with a capacity of 120 MW.
The possibility of building six additional icebreakers of the Icebreaker 8-9 class at the expense of investors to operate near the ports and terminals of the Western part of the Northern Sea Route at the mouth of the Yenisei River and in the Gulf of Ob is being considered. This will make it possible to free up more powerful autonomous nuclear-powered icebreakers to operate in the Eastern sector of the Northern Sea Route. The construction of the first four additional icebreakers is planned until 2030.
As a result, by 2030, the nuclear icebreaker fleet of Rosatom State Corporation will include 9 ultra-modern nuclear-powered icebreakers, while the total group of the Arctic icebreaker fleet in the waters of the Northern Sea Route by 2030 should be at least 13 units.
At the same time, work is underway to expand the Arctic cargo fleet. At the moment, 45 high-class cargo ships of the Arctic class are in operation. Taking into account the investment plans of shippers, by 2030 the number of vessels of the high Arctic class should increase to 132 vessels.
At present, the Zvezda Shipbuilding Complex is engaged in the construction of all types of sea vessels. In order to expand the capacity of the Russian shipbuilding industry, Rosatom State Corporation is working on the creation of a shipyard for the construction of specialized vessels and platforms for its own needs.
Particular attention is paid to the safety of navigation. For these purposes, it is planned to build 46 rescue vessels, the Arc5 multifunctional marine rescue vessel, Arctic helicopters of the Ministry of Emergency Situations, as well as the construction of rescue fleet bases in the ports of the Northern Sea Route.
The transformation of the NSR into a global transport system will increase the transport capacity and export potential of Russian products. It is especially important that the entire route of the Northern Sea Route passes through the territorial waters of Russia, which excludes the possibility of external pressure and makes the route as reliable as possible for the creation of new logistics chains.
In addition, the development of the NSR infrastructure will create "growth points" for the socioeconomic development of the Arctic regions and will contribute to the formation of new competencies for Russian industry and energy consumption centers. Thus, the NSR can become another powerful driver for the development of the entire Russian economy.
Currently, the .ru domain is undergoing a cyber attack that’s made access to the Kremlin and other news sites impossible, while others are crippled to some degree. Fortunately, this site only had its formatting and photos attacked. As noted, this article is to supply context for the next one on Arctic Development.
*
*
*
Like what you’ve been reading at Karlof1’s Substack? Then please consider subscribing and choosing to make a monthly/yearly pledge to enable my efforts in this challenging realm. Thank You!





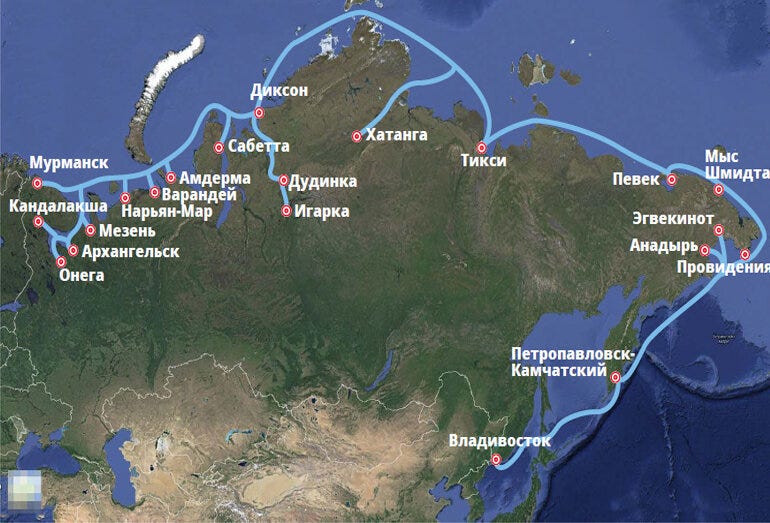
Thank you karlof. The northern sea route is extremely important to Russia so it might extend the linkages to the many isolated communities across those regions and enable year round supply for essentials. It alleviates poverty and profoundly integrates the Russian nation and national consciousness. It also enables a vast trading alternative for ships of the Russian or Chinese flag to trade their good. Other allies may get a share of that route as well at discounted ice breaker rates but it is likely to be less than a Suez crossing.
Importantly it is nice fu to the plundering hordes in Canada and the USA that so desperately covet those minerals and gasses and oils and broken states within Russia.
And today, to top it all off Lena Petrova brings good news:
https://rumble.com/v4adiaq--breaking-uae-china-transaction-settled-with-digital-dirham-uae-new-cbdc-in.html
I see I forgot to include the link to the Leader video--oops!! Here it is, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i9IO6fOI_ds